NEO:智能经济的东方以太坊
NEO,曾被称为“中国以太坊”,是一个旨在通过数字资产、身份和自动化构建智能经济的智能合约平台。本深度报道涵盖了NEO的历史、核心技术(包括dBFT和双代币设计)、生态系统增长、市场表现,以及从2025年到2030年的详细价格预测。无论您是在追踪其复苏还是考虑长期潜力,本指南概述了您需要了解的一切。
NEO的官方绿色标志已成为其作为智能合约和数字资产平台的身份的代名词。NEO是一个基于区块链的加密货币和开发平台,因其起源和类似目的而被誉为“中国以太坊”加密货币。2014年以AntShares的名义推出,2017年更名为NEO,是中国第一个开源公共区块链。NEO怀揣着一个“智能经济”的宏伟愿景——结合数字资产、数字身份和智能合约,彻底改变我们交换价值的方式。多年来,NEO的发展历程经历了早期炒作、技术升级、市场波动周期和不断发展的全球生态系统。本文深入探讨了NEO的历史、核心技术、市场表现和前景展望,包括NEO 2025年价格预测(短期)和NEO 2030年硬币预测(长期)。
NEO的历史:从AntShares到“中国的以太坊”
NEO的故事始于2014年,当时达鸿飞和张坤创立了一个名为AntShares的项目在中国。在早期,AntShares的目标是在区块链上数字化现实资产,并允许“智能合约” - 自动执行的代码,无需中介机构即可执行协议。这是一个与以太坊的能力相媲美的新颖构想,这使得AntShares获得了“中国以太坊”的绰号。到了2016年,团队已经将项目开源,并发布了一份白皮书概述他们的愿景。真正的突破是在2017年中期:AntShares进行了一次重大改版,以NEO的形式出现,将其身份与一个时尚的新标识以及一个新的“智能”经济概念相一致。
作为NEO,该项目迅速赢得了人气,特别是在中国加密社区中。在2017年和2018年初,NEO的价值在ICO热潮和对智能合约平台日益增长的兴趣中急剧上升。它经常被宣传为中国对以太坊的回应,受益于当地对区块链创新的热情。在这一时期,NEO的价格飙升(下文详细介绍)并且其市值进入了加密货币的前列。当时NEO的成功也得益于合作伙伴关系和强大的开发者社区(“Zion之城”小组)对其生态系统的贡献。到2018年,NEO已经牢固地确立自己作为一个全球公认的项目,并且许多人称之为“中国以太坊加密货币”,因为它的起源和可比较的功能。
核心技术和智能经济愿景
NEO平台的核心是一个强大的技术框架,旨在实现其智能经济愿景。NEO使用一种称为DeleGate.iod拜占庭容错(dBFT)的独特共识机制。在dBFT中,一组指定的节点(记账人)就交易达成共识,允许网络在几秒钟内确认区块。该方法比比特币的工作量证明更节能,并据称支持高吞吐量(潜在的每秒数千次交易)。NEO选择dBFT反映了去中心化和性能之间的平衡,迎合了数字金融等需要速度和可靠性的应用。
NEO的另一个独特之处是其双代币模型。NEO区块链拥有两种原生代币:NEO和GAS。NEO代币(简称NEO)代表对网络的所有权-它是不可分割的(不能分割成分数),总供应量为1亿枚代币(今天大约有7050万NEO在流通)。在钱包中持有NEO会随着时间自动生成GAS代币。GAS是用于支付交易费、部署和运行智能合约以及在NEO网络上推动运营的实用代币。该设计鼓励长期持有NEO(持有者获得GAS奖励),并在生态系统中将治理(NEO投票权)与使用(GAS支出)分开。
NEO的架构强调智能合约和互操作性。开发者可以在NEO上使用多种编程语言(如C#,Python,Java和Go)编写智能合约,这要归功于通用的NeoVM(Neo虚拟机)。这种多语言支持降低了开发者的门槛(与以太坊最初的Solidity-only方法不同),并帮助吸引了广泛的开发者群体。该项目的整体愿景是“智能经济”,包括数字资产,数字身份和智能合约三大支柱。
实际上,这意味着现实世界资产可以在NEO的区块链上代币化(数字资产),参与者可以将他们的真实身份或证书与这些资产关联(数字身份),业务逻辑可以通过代码自动执行(智能合约)。例如,土地所有权可以表示为NEO代币,与所有者的经过验证的身份关联,并通过智能合约规则进行转让或用作抵押品-全部在链上。这一全面的愿景使NEO不仅仅是一种加密货币;它旨在成为下一代商业和金融的综合生态系统。
多年来,NEO一直在升级其核心技术。一个重要的里程碑是推出了NEO 3.0(Neo N3),这是一个重大更新,旨在提高性能、安全性和功能。Neo N3引入了增强功能,如去中心化文件存储(NeoFS)、链下数据的预言机和完善的治理机制。截至2021年至2022年,N3升级完成了迁移阶段,使NEO的平台更具可扩展性和开发者友好性。它还为NEO上的新用例和dApps 蓬勃发展奠定了基础,符合该项目成为智能经济基础的长期目标。
生态系统和使用案例
NEO的生态系统涵盖了各种基于其区块链构建的用例和项目。在2017年至2018年的繁荣期间,许多ICO和代币(在NEO上称为NEP-5代币,类似于以太坊的ERC-20)被推出。其中包括去中心化交易所、身份验证项目和数据共享平台。一个值得注意的例子是Red Pulse(PHX),这是NEO上的第一个代币销售,旨在提供市场情报。在接下来的几年里,生态系统扩展到覆盖去中心化金融(DeFi)、游戏和数字收藏品。
例如,NEO看到了Flamingo Finance (FLM)的出现,这是一个在NEO网络上提供流动性挖矿和交换的DeFi平台。此外,NFT和游戏项目利用NEO的快速确定性和免费(或低成本)交易,提供了用户友好的体验。
NEO的一个核心用例是创建和管理数字资产。企业或个人可以在NEO区块链上发行代表股份、商品或其他资产的代币。由于NEO内置的数字身份功能,如果发行者将代币持有与经过验证的身份关联,这些资产可以合法合规。这为受监管的资产如证券或房地产潜在地利用NEO网络打开了大门。
这个想法是,股票发行、众筹或贷款合同可以通过NEO智能合约运行 - 自动化合规(通过数字身份验证)和结算(通过代币交易)。
NEO 生态系统以社区驱动的发展而闻名。Zion 城市开发者社区和 NEO 全球发展(NGD)通过资金和技术指导支持新项目。NEO 的团队启动了 EcoBoost 等项目,为在 NEO 上构建的初创企业提供资助和孵化。因此,开发了多个 dApp、钱包和基础设施工具。
例如 NeoLine 和 O3 钱包用于管理 NEO 和 GAS,以及 NeoTracker,一个区块链浏览器。此外,互操作性一直是重点 - NEO 是 Poly Network 联盟的一部分,可以实现跨链资产转移,并引入了与其他区块链和传统系统交互的功能。
从用户的角度来看,持有NEO本身就是一种用例:NEO持有者会自动赚取GAS,可以领取、使用或出售。这种机制经常被比作股息或抵押奖励,并激励参与网络治理(因为NEO持有者可以投票选举共识节点)。总的来说,NEO的用例涵盖了金融和游戏中的去中心化应用,数字身份解决方案以及通证化的现实资产。尽管其生态系统规模不及以太坊,但NEO在亚洲市场特别是在智能经济理念方面开辟了一小块市场,并不断看到与其智能经济理念相符的新项目和整合。
市场表现和价格历史
NEO的市场表现一直充满了戏剧性的高低起伏,既反映了项目的里程碑,也反映了加密市场的整体波动性。在早期交易日(2016年末),NEO(当时的AntShares)的价格仅为几美分。随着项目于2017年中更名为NEO并引起全球关注,其价格从2017年初不到1美元上涨到年底的数十美元。真正的爆发发生在2017年底至2018年1月的加密牛市期间:NEO的价格呈指数增长,于2018年1月中旬达到约180-200美元的高点(有史以来最高)。这一惊人的涨势使早期投资者获得了巨大回报,并巩固了NEO当时作为顶级加密货币的地位。
然而,在2018年整个加密货币市场进入熊市阶段后,NEO的价格迅速下跌。到2018年底,NEO的价格已经暴跌至大约7-8美元左右,彰显了加密资产的极端波动性。

图表:自2016年至2025年初NEO的历史价格走势(美元)。NEO在2018年1月迅速上涨至近200美元,随后在2018年熊市期间急剧下跌。2021年上半年出现第二波价格飙升(最高约140美元),之后又一轮下跌趋势将价格拉至2023年至2025年的个位数水平。
2018年底触底后,NEO出现了轻微的复苏和稳定。2019年,其价格大多在大约5美元和20美元之间波动,在中期出现了一个小幅增长(NEO在2019年中期市场短暂反弹时达到约20美元)。2020年,加密货币和DeFi再次引起了人们的兴趣,NEO参与了这一增长:在2020年夏季,它的价格达到了近25美元的本地高点。
更为重要的是,2021年的普遍牛市再次推高了NEO。到了2021年4月至5月,NEO暴涨至约120美元至140美元之间,乘着对另类币的热情和对Neo N3升级的期待。尽管这次2021年的高峰低于2018年的纪录,但仍然是一个显著的复苏。然而,与之前的模式一样,随后出现了市场范围的调整。直至2021年末和2022年,NEO的价格持续下滑。
2022年对许多加密货币来说是残酷的一年(例如市场崩盘和全球经济收紧等事件);NEO从2022年初的大约25美元跌至2022年底的大约6美元左右。到2023年,NEO的价格在个位数到两位数之间徘徊。偶尔会出现一些反弹(例如,NEO在2023年曾一度飙升至约15美元,因为加密市场短暂反弹),但总体而言,它仍远低于以前的高点。
进入2024–2025年,NEO一直在中个位数美元交易。截至2025年中期,NEO的价格在5–6美元区间,比其最高价下跌超过97%。其市值使其在全球中级加密货币中排名较高(到2025年,它已跌出前50名,反映自其鼎盛时期以来许多新项目的出现)。从高点急剧下跌既说明了围绕NEO的炒作降温,也说明了智能合约平台领域的激烈竞争。
尽管价格波动较大,值得注意的是NEO仍然保持着一批忠实的持有者和活跃的网络。在最大供应量为1亿的情况下,大约有7000万NEO代币在流通,那些相信NEO长期愿景的人继续持有并产生GAS。上面的历史价格图表生动地展现了NEO的过山车般历程——2017年急剧上升,2018年初剧烈高峰,2021年次高峰,然后逐渐下降至当前水平。那些在最初阶段(NEO价格低于0.50美元)入场的投资者目前仍然盈利,价格为5美元,但很多在高峰期购买的人都遭受了重大损失。这段历史表明,未来的预测必须谨慎,因为NEO的过去显示了市场情绪可以迅速改变的情况。
NEO 2025–2026价格预测(短期)
短期内,大约覆盖2025年和2026年,NEO价格前景将在很大程度上取决于更广泛的市场周期和NEO自身的发展进展。到2025年,如果历史周期性趋势(比如围绕比特币减半事件的趋势)重复,加密市场可能会进入一个新的牛市阶段。如果2025年至2026年发生广泛的涨势,考虑到其已建立的名声和坚实的技术基础,NEO可能会参与其中。
在牛市情况下,NEO在2025年的价格预测可能会回升到两位数美元。例如,如果投资者对具有发展活动的旧平台恢复信心,NEO可能会在2025年底回升至10美元至20美元的范围内。这意味着其价格将从2025年年中的5美元水平上涨大约2倍至4倍,这在强劲的市场上涨中是可能的。
多种因素可能推动这种短期增长。首先,对智能合约平台的重新关注往往会提振该领域的所有主要参与者——如果以太坊、Solana等发起反弹,NEO也可能受益,因为交易员寻找被低估的替代品(“中国以太坊”的叙事可能再次出现,吸引投机资本)。其次,具体的发展里程碑,比如NEO上的新高知名度dApps或成功实施新功能(也许是AI和区块链的整合,正如NEO的创始人所暗示的),可能改善市场情绪。如果NEO表现出增长的链上活动——更多交易,更多GAS使用——这将表明真正可以证明价格上涨的采纳。
到2026年,假设加密货币市场仍处于扩张阶段,NEO有可能会进一步上涨。对于2026年的乐观NEO价格预测可能会将目标定在20美元至30美元的范围内。这仍然只是NEO昔日辉煌的一小部分,但相比目前水平来说代表了可观的增长。用数字来表示,25美元相当于从5美元增长了5倍。这一水平也与一些历史阻力相吻合(NEO在2019年和2020年的高峰期间曾达到20美元以上),如果势头增强,这可能是一个现实的中期目标。
需要注意的是,这些数字是推测性的——它们假设市场条件有利。在更为保守的情景中,如果加密货币市场停滞或者NEO未能吸引新的兴趣,到2025年至2026年,其价格可能仅在高个位数范围内徘徊,或许在7美元至10美元之间。短期内的下行风险包括持续低需求、更强大的竞争夺走开发者和用户,或者一般的熊市力量。
总体而言,NEO的短期预测趋向谨慎乐观:如果整体加密货币环境改善并且NEO在生态系统增长方面取得进展,未来几年内恢复到大约15至25美元是可行的。然而,交易者应该牢记NEO的波动历史以及需要持续的正面消息来推动任何反弹。
NEO币预测2030:长期展望(2027–2030)
展望2027年至2030年,NEO币2030年预测考虑了NEO在长期内可能的表现。到本十年末,加密货币格局可能会大不相同——区块链技术可能会更加融入日常系统,只有具有强大实用性和社区的项目才有可能蓬勃发展。
如果NEO成功保持相关性并在智能合约平台市场中占据重要份额,其长期价格可能会大幅上涨。一些分析师和社区预测认为NEO有可能在2020年代末重新访问先前的历史最高价,这意味着在极其看涨的情况下可能回到100美元以上的范围。例如,一个乐观的预测认为NEO在2029年至2030年间可能达到80至100美元左右,假设NEO基于应用程序得到全球主要采用,并在其中发生了几次强劲的牛市。
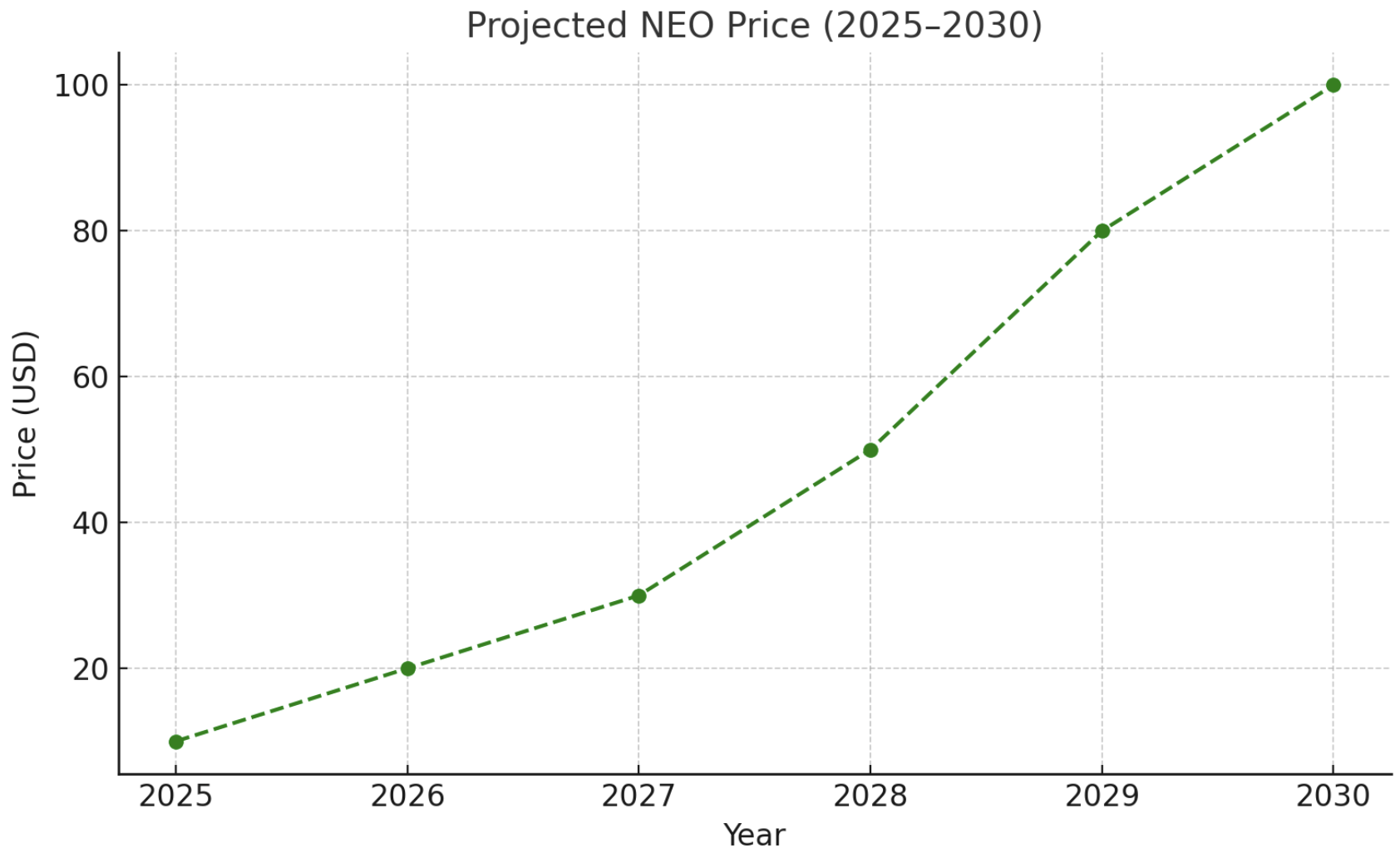
图表:2025年至2030年NEO价格预测轨迹(仅供参考情景)。该预测假设逐渐增长,并在2020年代末加剧,NEO有望在2030年达到约100美元。早期(2025年至2026年)显示适度恢复至10美元至20美元范围,而后年(2027年至2030年)考虑到更广泛的加密货币采用和NEO生态系统的成熟,加速价格上涨。
在一个有利的长期情形下,到2027年至2028年,NEO的价格预测可能会看到该币攀升至30美元至50美元的范围。这一水平可能会受到NEO智能经济愿景成熟的推动,例如,如果到2027年,有许多企业或政府相关项目在NEO的网络上运行(用于数字身份或资产代币化),NEO和GAS的需求可能会激增。
此外,NEO的固定供应意味着任何对需求的显着增加都必须通过价格上涨来满足,因为除非有剩余的非流通供应正在逐渐释放(如果适用),否则不会有新的NEO代币涌入市场。到2028年,如果NEO保持强大的生态系统,人们可以想象它重新获得前20的市值位置,这在历史上可能对应着十美元或更高的价格,具体取决于整个加密市场的规模。
随着我们逼近2029年至2030年,投机性预测往往目标高远。如果几个条件得以顺利对齐,NEO在2030年达到100美元的想法并不荒谬:一个蓬勃发展的Neo N3生态系统,拥有数十个受欢迎的dApps,亚洲地区有重要的机构或政府采用NEO技术(例如,智能城市使用Neo进行数字身份证或供应链管理),以及整体加密货币市场繁荣,推动所有主要平台。
100美元的价格意味着NEO的市值会增长巨大(取决于当时的流通供应量,可能超过70-80亿美元),如果到2030年整个加密货币市值达到数万亿(正如一些人预测的在完全实现的Web3世界中)。然而,这样高的预测伴随着重大的不确定性。
一个更为保守的长期展望可能会将NEO的定位放在其2018年中期水平左右 - 也许到2030年时在30美元至50美元的范围内,如果它继续使用但并不主导。这依然将是一个非常健康的增长,从今天的5美元价格(增加6倍至10倍),并且将表明NEO找到了一个稳定的利基。
如果NEO无法跟上竞争对手,也有可能停滞或进一步下跌。新一代智能合约平台(甚至是Ethereum的迭代版本)在技术上可能会使NEO相形见绌,从而限制其采用率。如果NEO的开发者社区萎缩,或者dApp活动保持低迷,那么即使整体市场增长,到2030年,NEO的价格可能会在个位数或低青少年水平上徘徊。
总的来说,NEO的长期预测是谨慎乐观的,但高度依赖执行力。在看涨的情况下,NEO到2027年有可能交易在几十美元,可能在2030年接近100美元,重新夺回在加密生态系统中的重要地位。这假设NEO继续创新(超越N3的更新),吸引新的应用程序,并从定期的加密市场牛市中受益。
相反,如果NEO未能显着增加其用户群或在众多区块链网络中脱颖而出,那么从现在起的五到十年内,其价格可能只会略有改善(甚至可能会下滑)。投资者在关注2027年至2030年的时候,应该将NEO的链上指标和生态系统增长作为其长期价值的关键指标。